Introduction
The India US trade war 2025 represents a pivotal moment in international commerce, as President Trump’s administration implements sweeping 25% tariffs on Indian exports. This escalating trade conflict between two major economies has triggered comprehensive strategic responses from India, reshaping bilateral trade dynamics and forcing a reassessment of global supply chains. Understanding the implications of the India US trade war 2025 is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and economists worldwide.
Executive Summary: India US Trade War 2025 Overview
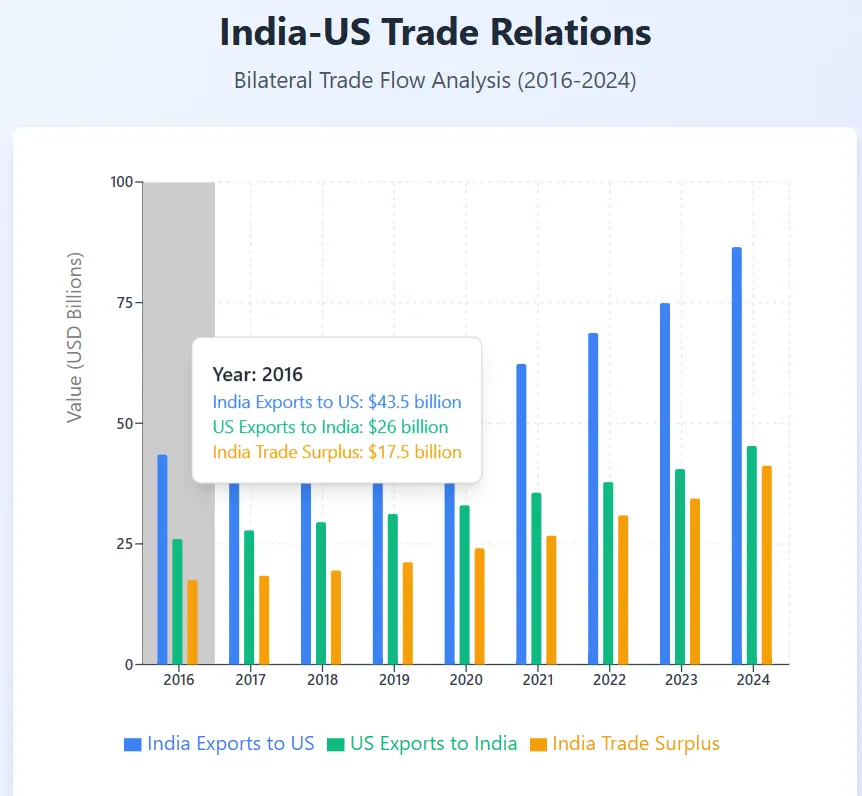
In early 2025, the United States implemented a substantial 25% tariff on Indian exports under President Donald Trump’s renewed administration, accompanied by penalties related to India’s energy and defense partnerships with Russia. This comprehensive analysis examines India’s measured and strategic response to these trade restrictions, which pose significant challenges to the nation’s export-driven economy.
Background and Trade War Context
The India US trade war 2025 tariff implementation followed a period of escalating trade tensions that began in January 2025. The Trump administration’s hardline trade policy initially involved threats of tariffs, a temporary pause in April, and eventual implementation by July 2025. During this period, India systematically prepared for potential trade disruptions by analyzing vulnerabilities in critical sectors, including textiles, gems and jewelry, and industrial machinery.
The US strategy extends beyond India, targeting multiple nations, including China, Canada, Mexico, and other BRICS allies through a comprehensive framework of tariffs and sanctions. The administration’s stated objectives include reducing the US trade deficit, pressuring nations with ties to sanctioned states like Russia, and establishing what it terms “reciprocal” trade arrangements.
India’s Five-Pillar Strategic Response to US Trade War 2025
1. Diplomatic Engagement and Negotiation
India maintains its commitment to diplomatic resolution, actively pursuing discussions for a more balanced and mutually beneficial trade agreement. This approach demonstrates India’s preference for collaborative solutions over adversarial responses.
2. Market Diversification Initiative
The government has accelerated efforts to reduce economic dependence on the US market by encouraging exporters to explore opportunities in Southeast Asia, Africa, and Europe. Priority sectors for diversification include apparel, gems and jewelry, and industrial machinery.
3. Retaliatory Measures and WTO Mechanisms
While maintaining diplomatic channels, India has preserved the option to implement retaliatory tariffs in accordance with World Trade Organization regulations. Although historical precedent suggests limited effectiveness of global dispute mechanisms, this strategy serves as an important diplomatic leverage tool.
4. Future Trade Agreement Safeguards
Policy experts recommend incorporating clawback clauses in future trade agreements, enabling India to withdraw benefits or demand renegotiation in response to unilateral tariff impositions.
5. Domestic Competitiveness Enhancement
The government is prioritizing support for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) through tax incentives and improved credit access. These measures aim to strengthen India’s capacity to absorb external economic shocks while maintaining export momentum.
Economic Impact Assessment of India US Trade War 2025
The India US trade war 2025 tariff implementation presents significant challenges to India’s economic outlook:
Projected Export Losses: $30-33 billion annually
GDP Growth Impact: Estimated decline of 0.2-0.4 percentage points
High-Risk Sectors: Jewelry and gems, textiles, automotive components, industrial machinery
GDP Projection: Potential decline below 6% for fiscal year 2025-26
Strategic Implementation Framework for Trade War Recovery
Short-term Adaptive Measures
- Export Policy Adjustments: Guidance for exporters to pivot toward alternative markets and reduce US market exposure
- Monetary Policy Support: Reserve Bank of India’s accommodative stance to maintain domestic demand and investment stability
- Multilateral Coalition Building: Collaboration with similarly affected nations to counterbalance US trade leverage
Long-term Structural Reforms
- Value-Added Manufacturing Focus: Emphasis on higher value-added production and digital services exports, sectors with reduced tariff vulnerability
- Trade Bloc Development: Exploration of new regional and multilateral trade partnerships
- Economic Resilience Building: Strengthening domestic supply chains and reducing import dependencies
Conclusion: Navigating the India US Trade War 2025
India’s response to the US tariff implementation demonstrates a sophisticated understanding of contemporary trade dynamics. Rather than pursuing reactive measures, the government has adopted a comprehensive strategy that balances immediate economic protection with long-term structural positioning.
The multi-dimensional approach encompasses diplomatic engagement, economic diversification, policy innovation, and domestic strengthening. This strategy positions India to not only navigate current trade challenges but also emerge with enhanced global integration capabilities and greater economic self-reliance.
As the international trade landscape continues to evolve, India’s measured response exemplifies how emerging economies can transform trade challenges into opportunities for strategic repositioning and sustainable growth. The ongoing India US trade war 2025 will likely serve as a defining moment for future bilateral trade relationships and global economic cooperation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the scope and timeline of the US tariff on Indian exports? A: The United States implemented a 25% tariff on Indian exports in July 2025, following months of escalating trade tensions that began in January 2025. The tariffs are accompanied by additional penalties related to India’s partnerships with Russia.
Q2: Which Indian industries are most affected by these tariffs? A: The most vulnerable sectors include jewelry and gems, textiles, automotive components, and industrial machinery. These industries face significant export challenges due to the substantial cost increase imposed by the 25% tariff.
Q3: How much economic impact is India expecting from these tariffs? A: India anticipates export losses of $30-33 billion annually, with GDP growth potentially declining by 0.2-0.4 percentage points. The overall GDP growth may fall below 6% for fiscal year 2025-26.
Q4: What alternative markets is India targeting for export diversification? A: India is actively encouraging exporters to explore opportunities in Southeast Asia, Africa, and Europe, particularly in sectors like apparel, gems and jewelry, and industrial machinery to reduce dependence on the US market.
Q5: Will India impose retaliatory tariffs on US imports? A: While India has preserved the option to implement retaliatory tariffs in accordance with WTO regulations, the government currently prioritizes diplomatic engagement and negotiation for a mutually beneficial trade agreement.
Discussion Questions for Readers
- Strategic Trade Policy: How effectively can emerging economies like India balance diplomatic engagement with economic self-protection when facing unilateral trade restrictions from major powers?
- Market Diversification Challenges: What are the practical limitations and opportunities for Indian exporters in rapidly pivoting from the US market to alternative regions such as Southeast Asia and Africa?
- Global Trade Architecture: In what ways might India’s response to US tariffs influence the broader evolution of international trade relationships and multilateral trade agreements?
- Economic Resilience: How can developing nations build more robust economic structures to withstand sudden trade policy changes from major trading partners?
- Long-term Competitiveness: What role should domestic policy reforms play in enhancing a country’s ability to compete globally while reducing vulnerability to external trade pressures?




